Selecting a Syringe
Syringe Types
MedOfficeDirect carries a large variety of syringe types, depending on your medical need. Some syringes are used with a needle for injections and others are used without a needle for irrigation purposes or with tubing. Different syringe types include:
- Ear
- Dental/Oral
- Diabetic/Insulin
- Irrigation
- Spinal
- Epidural
- Catheter
- Standard
- Safety
- Tuberculin

Syringe Tips
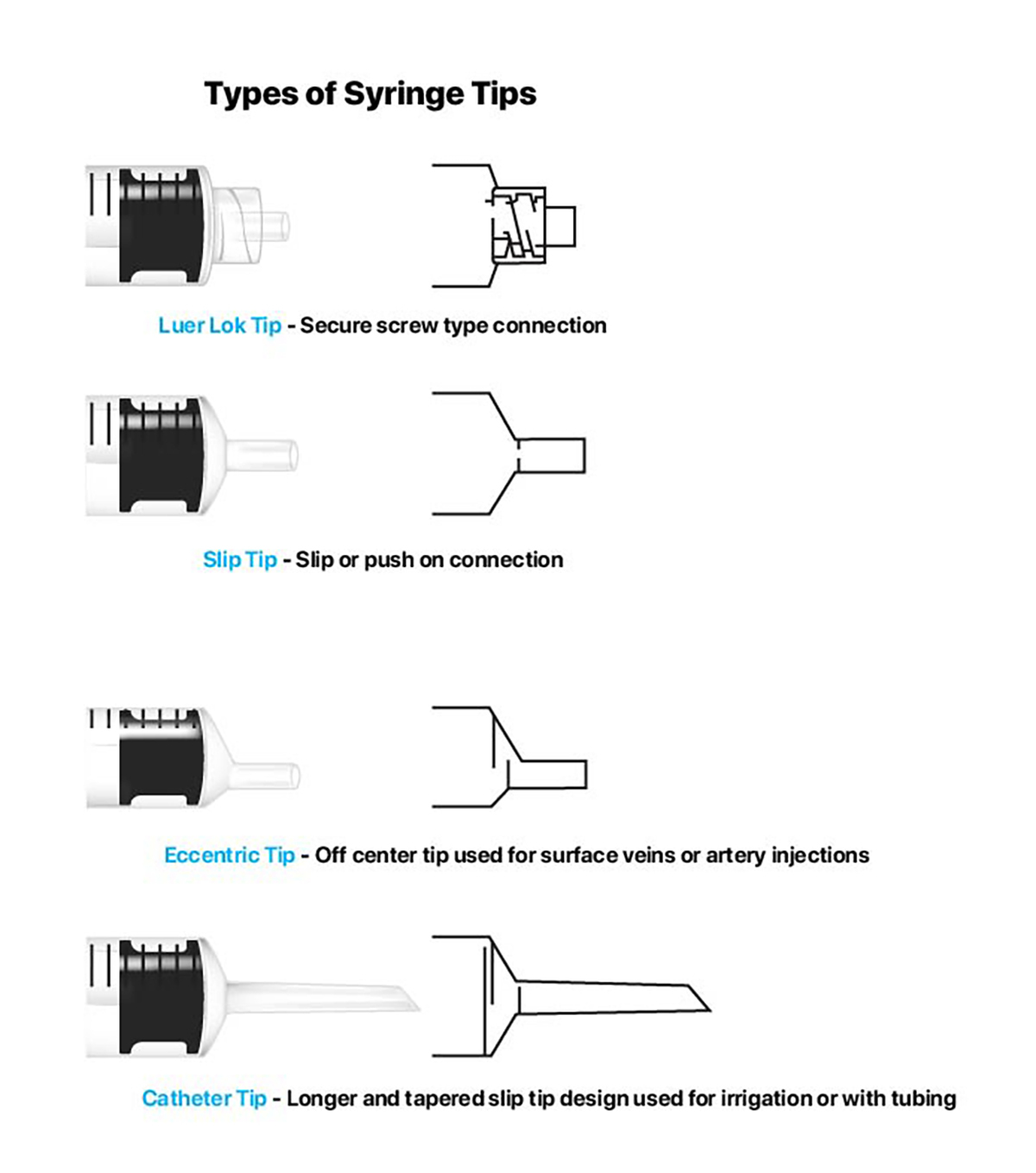
Syringe tips are available in multiple sizes and types:
- Luer Lok: With this locking style tip, needles are inserted into the syringe and twisted onto the tip to be locked into place. Luer Lok tips prevent liquids from leaking and prevent accidental removal of the needle.
- Slip Tip: This tip allows the needle to be easily pushed directly onto the end of the syringe tip.
- Eccentric Tip: This tip allows the attached needle to be parallel with the injection surface due to its off-center placement.
- Catheter Tip: Most often used for irrigation, this tip is longer and tapered at the end for use with tubing.
Syringe Sizes
Syringes sizes are based on their liquid capacity, measured in cc or mL. Capacity should be chosen depending on the volume and pressure or flow needed. Larger capacity syringes will have a lower pressure flow and fit a larger quantity of medication, while smaller capacity syringes have higher pressure and are typically used for subcutaneous and intramuscular injections.
Needle Sizes
Needles are available in a variety of lengths and widths, or gauges.

Needle Gauge and Length
Needle gauge sizes indicate the diameter or width of the needle and are measured differently than syringes. The smaller the gauge the larger the needle, meaning a larger gauge would denote a smaller width needle. Needle gauge is chosen based on the thickness and depth of the injection.

The best needle length choice is determined by the type of injection being performed:
- Intramuscular injections are inserted into the muscle and most commonly require a longer needle length and thicker needle, or high gauge.
- Intradermal injections typically require a shorter needle length and higher gauge as this type of injection is only inserted into the outer layers of the skin.
- Subcutaneous injections go into the tissue right below the skin and typically use a small, short needle.
